Introduction: When Numbers Dance to a Beat
You may not think of math while swaying to your favorite song, yet behind every chord, rhythm, and melody lies a hidden world of numbers and patterns. From the soulful ragas preserved through centuries to the vibrant rhythms of today’s films, music and math are inseparable companions. They may speak in different languages, but they share the same essence—structure, rhythm, and balance. Even more fascinating is how these patterns connect with the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine—the “feel-good” chemical—whenever we hear something truly delightful.
What Do We Mean by 'Math in Music'?
At its core, music is mathematical. Every rhythm, scale, and harmony follows patterns that can be described numerically. Here are a few key examples:
- Rhythm: Dividing time into beats (e.g., 4/4, 3/4 time signatures).
- Frequencies: Notes are sound waves with specific frequencies. For instance, the note A above middle C vibrates at 440 Hz.
- Ratios: Musical intervals are based on ratios, such as the octave (\( 2:1 \)) or the perfect fifth (\( 3:2 \)).
When we listen to music, our brain unconsciously processes these mathematical relationships, finding comfort in repetition and excitement in variation.
Patterns, Variation, and Dopamine
The brain thrives on patterns, but it also craves novelty. Music keeps us hooked by balancing repetition with surprise. Consider a simple sequence of notes: if a pattern repeats four times and then suddenly changes, our brain rewards us with a dopamine rush for recognizing the twist.
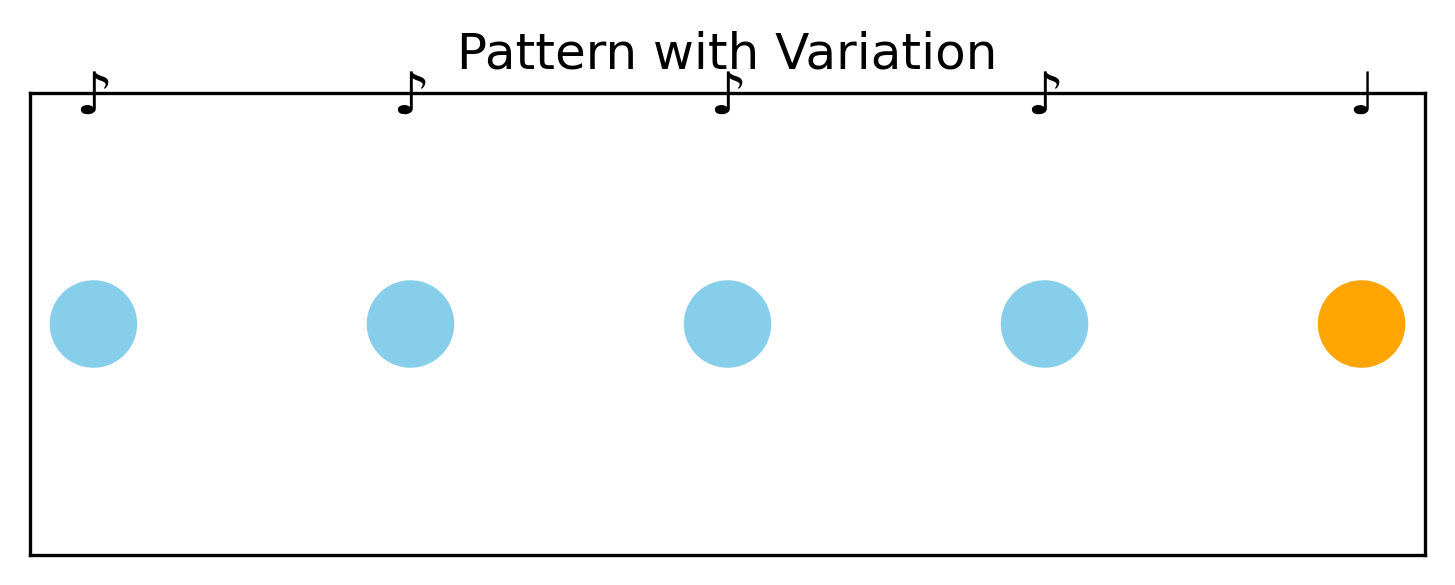
This visualization shows a sequence of four identical notes (♪) followed by a variation (♩). The repeated notes build expectation, while the final change creates a pleasurable surprise—just like a punchline in a joke or a plot twist in a story.
Daily Life Applications
Understanding the math behind music and its dopamine connection isn’t just theoretical—it plays out in everyday life:
- Mantras & Chants: Repetition with gentle variation in spiritual chants creates a meditative rhythm that engages the mind while calming the soul.
- Exercise & Focus: Rhythmic, repetitive beats in workout or study playlists help regulate brain activity and motivation.
- Learning & Memory: Songs with predictable patterns (like ABC rhymes) make it easier to remember information.
- Emotional Regulation: Surprising key changes or rhythmic breaks can evoke powerful emotional responses, helping us process feelings.
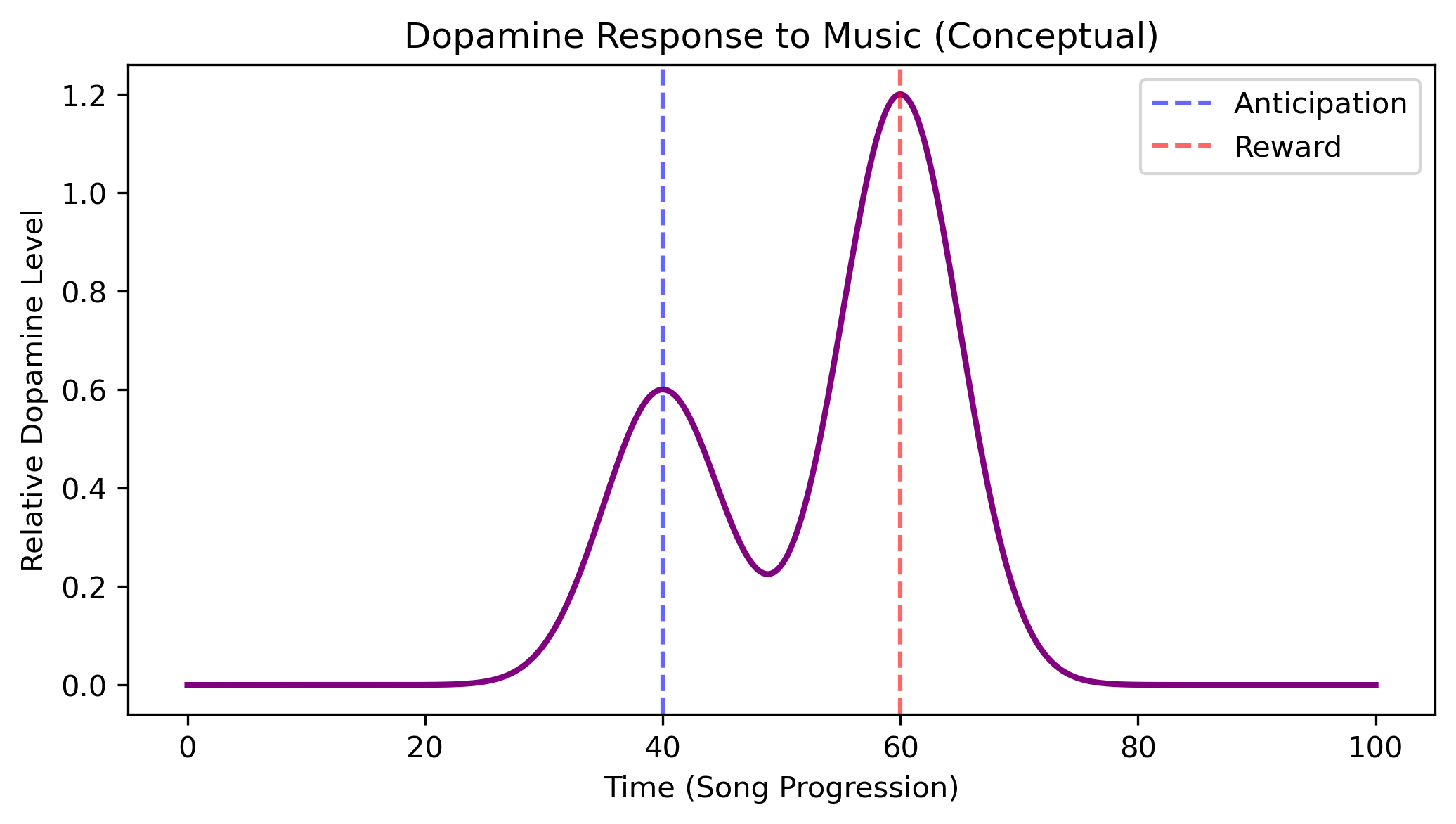
This kind of plot (dopamine vs. time) would show how the brain’s reward signal spikes at the moment of variation in a predictable musical sequence.
Comparison: Math in Music vs. Math in Other Arts
Math shapes more than just music—it also underpins art, architecture, and poetry. But here’s the difference:
- Music: Patterns are temporal, unfolding in time. Surprise comes as you anticipate the next beat or note.
- Visual Art: Patterns are spatial, seen all at once (e.g., symmetry in Islamic mosaics or the golden ratio in paintings).
- Poetry: Rhythm and rhyme schemes mirror the mathematical structure of music, but in language instead of sound.
Among these, music has the most direct connection with dopamine because it operates in real-time, constantly playing with our expectations.
Conclusion: Where Math Meets Emotion
Math in music is not just about abstract numbers—it’s about how those numbers translate into rhythm, harmony, and ultimately, joy. Repetition comforts us, variation excites us, and together they form the heartbeat of musical beauty. Next time you feel chills during your favorite song, remember: your brain is dancing with math and rewarding you with a hit of dopamine.